
But for practical purposes, a good rule of thumb is about 10 pK a units. So how far can we stretch this? In between these two extremes, at what point does a reaction become irreversible for practical purposes? At What Point Does An Acid-Base Reaction Become Irreversible For Practical Purposes? In other words, both species are present in solution. So the equilibrium constant here would only be about 10 to the power of 1.2 -> 15.8 toward giving the weaker acid (CH 3OH) and the weaker base HO(–).Īt equilibrium we’d expect to have a mixture of about 94% HO(-) and 6% H 3CO(-). Here we’re dealing with a very small difference in pK a – only 1.2 pK a units. Neither side of the acid-base reaction is strongly favored. What about the other extreme: the reaction of methanol (pK a of 15.2) with sodium hydroxide (the conjugate base of water, pK a 14)? An Easily Reversible Acid-Base Reaction: Methanol (pKa 15.2) With Water (pKa 14) That is to say that HCl and NaOH are completely consumed when they react together, giving only H 2O and NaCl.

That’s a difference of about 22 pK a units – and since each pK a unit represents one order of magnitude, this reaction is favorable with an equilibrium constant of about 10 to the power of 22.įor all intents and purposes, a reaction with an equilibrium constant this huge is irreversible. Sodium hydroxide is the conjugate base of H 2O (pK a 14). How favorable is this reaction? We can make a rough estimate. HCl and NaOH react to give water and NaCl. And to it, we add (slowly!) a solution of water containing one mole of sodium hydroxide (the conjugate base of water, pK a 14). On one extreme, we have one mole of a really strong acid – let’s say hydrochloric aid (HCl), pK a –8.
#Naoh acid or base plus
An Irreversible Acid-Base Reaction: Strong Acid (HCl) Plus Strong Base (NaOH) Giving Water
An Easily Reversible Acid-Base Reaction: Methanol (pKa 15.2) With Water (pKa 14).
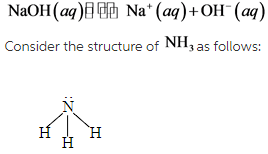
#Naoh acid or base how to
I also referred to a post on how to use a pK a table (key lesson: stronger acid plus stronger base gives weaker acid and weaker base). Last time we learned about pK a and how it’s the closest thing we have to a universal measurement of the strengths of all kinds of different acids and bases. Reversible And Irreversible Acid-Base Reactions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
